Scarlet Fever in Children. Dr. Narmin Azizova

Scarlet Fever is mainly observed in children aged 5-15 years. This disease is characterized by erythematous rashes that spread in combination with tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils) or skin infection. During Scarlet Fever, rashes appear both on the mucous membranes and the skin.
Causative Agent and Mode of Transmission
Scarlet Fever is caused by Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci. The disease spreads through airborne droplets and dust.
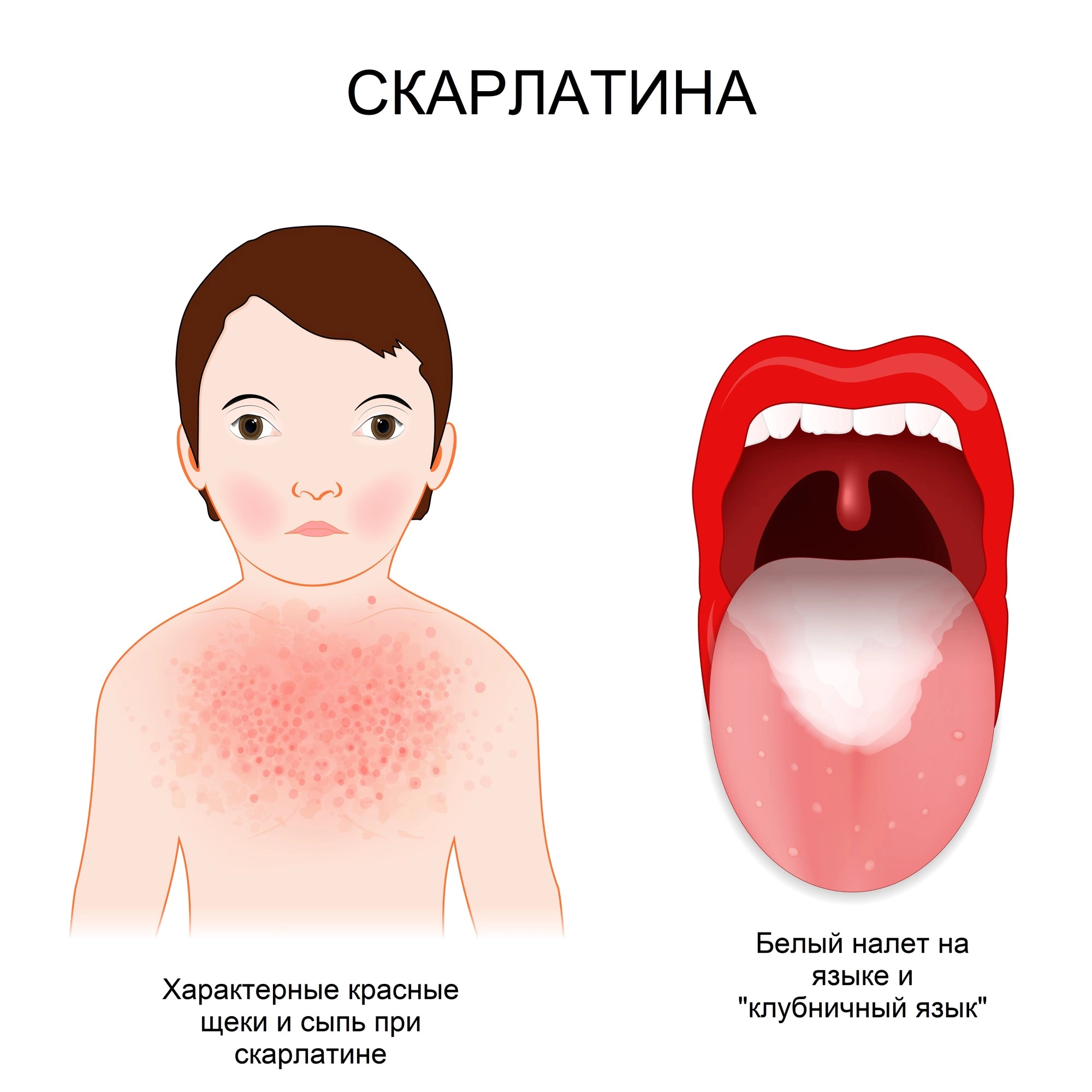
Clinical Symptoms
Symptoms usually appear 1-4 days after exposure. These symptoms include:
• High fever (above 38.3°C)
• Chills
• Sore throat
• Swollen and tender lymph nodes in the neck
• Headache
• Nausea and vomiting
• Abdominal pain
• Muscle aches
• Fatigue
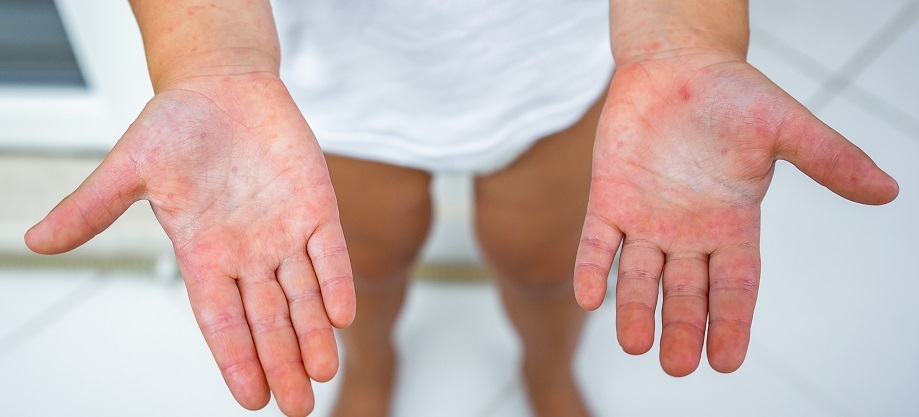
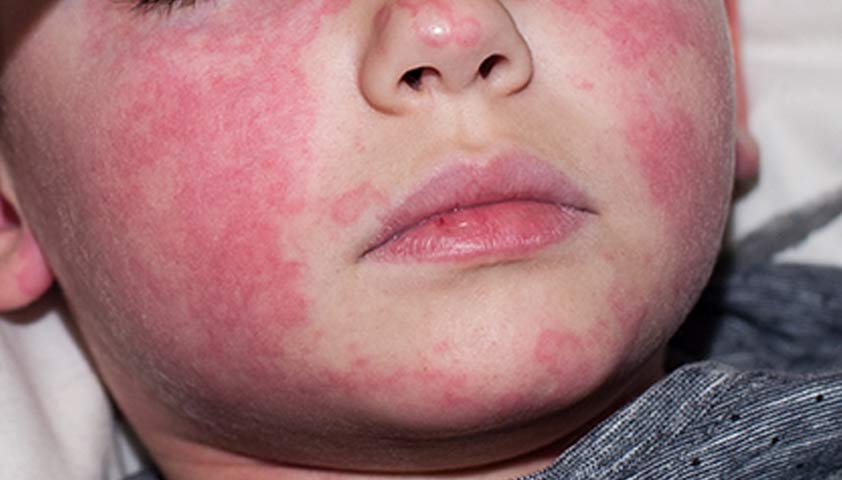
Rashes begin 6-48 hours after the onset of these symptoms. Initially, they appear on the head, neck, groin, and underarms. They then spread to other parts of the body. Rashes rarely spread to the face, but redness of the cheeks and paleness around the mouth can occur. The rash causes itching. The rash consists of very small (1-2 mm), raised, bumpy spots (like chicken skin) that blanch when pressed. Rashes are especially common in the palms of the hands (the palms) and, rarely, on the soles of the feet.
Tongue and Throat
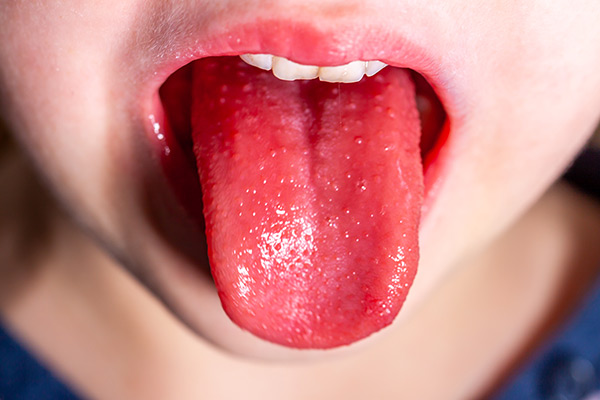
The throat exhibits swelling and redness, and rashes may also appear on the soft palate. During the first 1-2 days of the illness, the tongue is covered with a white coating (“white strawberry tongue”). After a few days, it turns into a red, “strawberry” tongue.
Course of the Rash
The rashes begin to fade after about 7 days. During this period, peeling of the skin on the fingertips and toes is observed. Skin peeling can last for several weeks.

Complications
Scarlet Fever can lead to several complications, including:
• Sinusitis (inflammation of the sinus cavities)
• Otitis media (inflammation of the middle ear)
• Inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes
• Acute rheumatic fever
• Acute glomerulonephritis
Treatment
The treatment of Scarlet Fever involves starting antibiotic therapy as prescribed by a doctor. After treatment begins, fever usually drops within 6-24 hours. The contagious period of the disease may end 24 hours after starting treatment.
